DATE: March 27-31, 2023 |
VENUE: Council for Technical Education and Vocational Training (CTEVT), Sanothimi, Bhaktapur, Kathmandu, Nepal |
ORGANIZERS: Colombo Plan Staff College (CPSC) and Council for Technical and Vocational Education and Training (CTEVT), Nepal |
PARTICIPANTS' PROFILE: The participants of this program will be composed of College Director / Deputy College Directors / Assistant College Directors, Administrators, Teachers / Instructors, and Lecturers assigned in Technical and Vocational Education and Training institutions and agencies in Nepal. |
The 21st century has changed people's lives, especially communication and education. The technological tools and platforms that have emerged in recent years have resulted in very complex and demanding social, economic, and academic lives, completely different from previous ones. These changes and characteristics of the new century require individuals to possess new skills, which are mostly referred to as 21st century skills including entrepreneurial skills. In education, students need to acquire and develop these skills because they should be ready to meet their demands when they graduate. In this new Era the “Fourth Industrial Revolution '' set a new momentum to the training and development sector. The revolution brings new exciting opportunities and solutions to global challenges such as automation of industrialization. It will also produce new jobs that have yet to be invented. The critical challenge for skills development is serious skills mismatches despite growing investments in TVET. Thus governments, educators and policy makers alike must ask the questions about how they can prepare present and future TVET to thrive in this digital world. Technical and Vocational Education & Training in the Fourth Industrial Revolution (TVET 4.0) is a complex, dialectical and exciting opportunity which can potentially transform society for the better. The fourth industrial revolution is powered by artificial intelligence and it will transform the workplace from tasks based characteristics to human centered characteristics. Because of the convergence of man and machine, it will reduce the subject distance between humanities and social science as well as science and technology. This will necessarily require much more interdisciplinary teaching, research and innovation in TVET. Therefore integrating 21st century skills along with entrepreneurship skills into educational institutes requires a thorough process. The demand for educational institutes to equip students with entrepreneurship & 21st century skills creates challenges in pedagogy and assessment. Therefore, this process requires careful planning. Curriculum, professional development, and assessment are central factors that need to be taken care of for successful implementation.
As in the Asia Pacific region CTEVT represents Nepal being an apex body of TVET and working day & night for the sustainable TVET. CTEVT is implementing the "Learn-Earn-Pay" modality in all TVET institutions. In this connection "Management of Business incubation in TVET institute” will play a successful role in implementation of "Learn-Earn-Pay" modality by understanding and applying business incubation in TVET Institutes that ultimately lead to sustainable development. But it is also important to understand that Instructors are the main actors in the TVET institutes to train the skilled workforce for the 21st Century and their role is very much critical in familiarizing & training the skilled workforce with the term entrepreneurs.
The Government of Nepal has set the motto of "Prosperous Nepal, Happy Nepalese". To strive for the success of this motto, Nepal is in need to develop self-sustainable, competitive, innovative, and value oriented citizens for the socio-economic transformation of the nation. This is possible only through sustainable TVET.
In simple words these Business Incubation Center (BIC) in TVET institutions can create a boom in skilled workforce life and sustainability to TVET because business incubators are programs designed to accelerate the successful development of entrepreneurial and technological skills through an array of business support resources and services, developed and orchestrated by incubator management and offered both in the incubator and through its network of contacts. Incubators vary in the way they deliver their services, in their organizational structure, and in the types of clients they serve.
Business incubators are seen as efficient tools for technology transfer and cooperation between the scientific sector and the industry. Generally, they are targeted towards addressing local economic development issues through improvement of the entrepreneurial base. Thus, TVET institutions need to have strong partnership with the business and industry to establish BIC either in their premises or in their own premises.
TVET institutions play a vital role in the generation of entrepreneurs and with the help of industries in shaping today’s students into tomorrow’s entrepreneurs. Collaboration between institutes and industries is critical for skills development (education and training), the generation, acquisition, and adoption of knowledge (innovation and technology transfer), and the promotion of business incubation centers. The benefits of institute-industry partnership is wide-reaching: they can help exploit synergies and bring intended outcomes of TVET institutions. Worldwide initiatives in TVET like technology business incubator, science parks, research parks, innovation centers are the latest in the evolutionary line of effective institute-industry partnership mechanisms. A Technology Business Incubator (TBI) is a form of business incubator that focuses on promoting technology-based business start-ups. With technological advancement in the 21st century, TVET institutions need to focus on producing technopreneurs who will be job providers rather than seeking employment. One of the best ways to achieve it is by establishing BIC in a partnership with industries and enterprises. Thus, CPSC in collaboration with CTEVT is organizing this in-country program to impart necessary concepts, integration processes, and guidelines to incorporate the very essential components in the design to share knowledge and TVET institutions’ good practices of BIC.
The participants are expected to:
- Understand the concept of business incubation center in TVET
- Explore the model of business incubation
- Understand the role of incubation center in TVET
- Provide necessary knowledge and skills of establishment and management of business incubation centers for TVET leaders
The Participants are expected to gain more knowledge, experience and enhance the capacity of TVET leaders to establish and manage the business incubation center at TVET institutes.
- Analysis of TVET Institute Image Building with 21st Century Environment
- Competency Based Training Framework for Business Incubation
- Business Incubation Model
To achieve the objectives set forth, the following strategies will be employed in a consultative nature
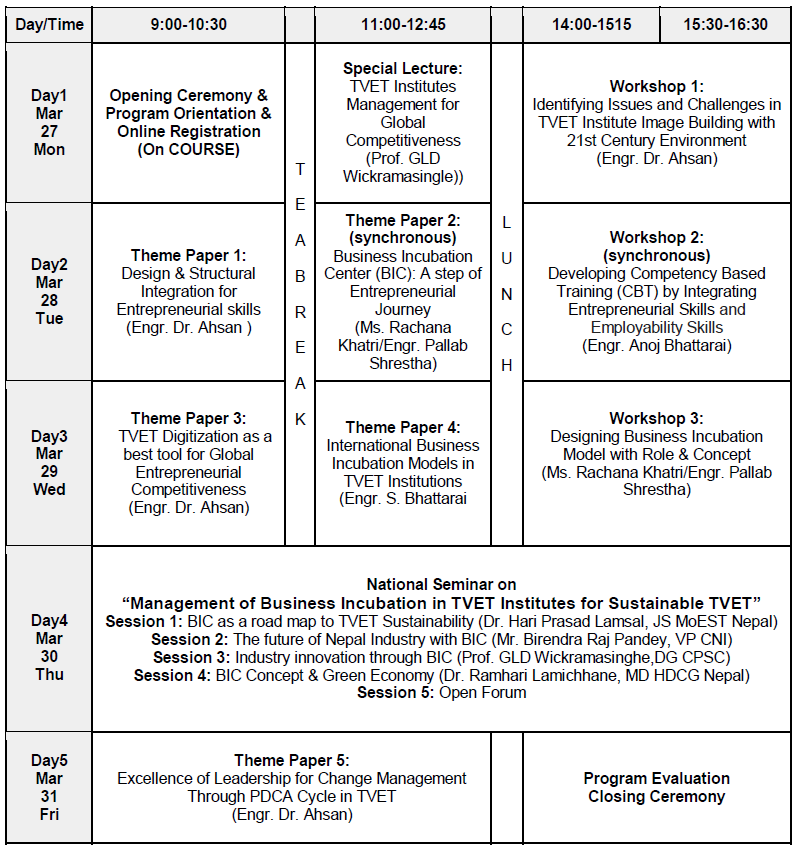
Theme Paper (TP) Presentations on the following:
- Special Lecture: TVET Institutes Management for Global Competitiveness
- Theme Paper 1: Design & Structural Integration for Entrepreneurial skills
- Theme Paper 2: Business Incubation Center (BIC): A step of Entrepreneurial Journey TVET & Digitization
- Theme Paper 3: TVET Digitization as a best tool for Global Entrepreneurial Competitiveness
- Theme Paper 4: International Business Incubation Models in TVET Institutions
- Theme Paper 5: Excellence of Leadership for Change Management through PDCA Cycle in TVET
Workshops (W)
- Workshop 1: Identifying Issues and Challenges in TVET Institute Image Building with 21st Century Environment
- Workshop 2: Developing Competency Based Training (CBT) by Integrating Entrepreneurial and Employability Skills
- Workshop 3: Designing Business Incubation Model with Role & Concept
National Seminar on “Management of Business Incubation (BIC) in TVET Institutes for Sustainable TVET”
- Session 1: A BIC as road map to TVET Sustainability
- Session 2: The future of Industry with BIC
- Session 3: BIC Concept & Green Economy
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|